Many of the guys must have thought that how does generator works? Well, today we are going to answer all your queries about how the generator produces electricity and its inner workings.
Let’s start from the beginning. Any portable generator is made up of many parts including, an engine, fuel source, alternator, and power outlets.
The fuel is ignited in the engine and using this energy; the mechanical gears drive the rotor of the alternator which, then cuts the magnetic flux of the stator. After which the voltage is induced in the coils and electricity is produced.
Confused? Well, you should be because this process is a whole lot complicated than it sounds. We will discuss this phenomenon in detail later.
The generator also has a speed regulator that controls the speed of the generator shaft. Also, there must be a cooling system and lubrication for moving parts.
First of all, let us understand how electricity is produced in the generator and then we will explain its different parts.
Read Also,
- Best Propane Generator
- Best Westinghouse Generator
- Reviews Difference Between Conventional Generator And Inverter Generator
How electricity is produced in a generator?
I will try to explain things in as simple terms as possible, so don’t worry.
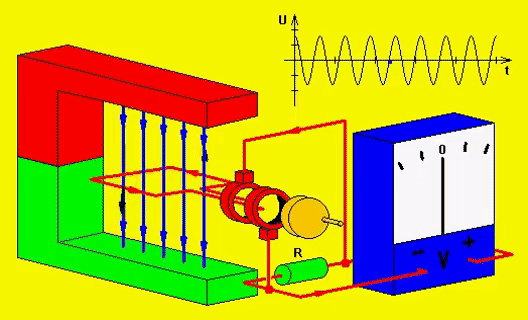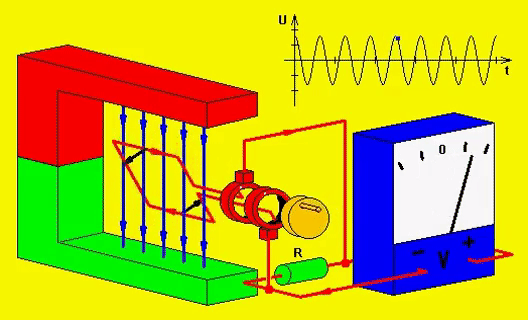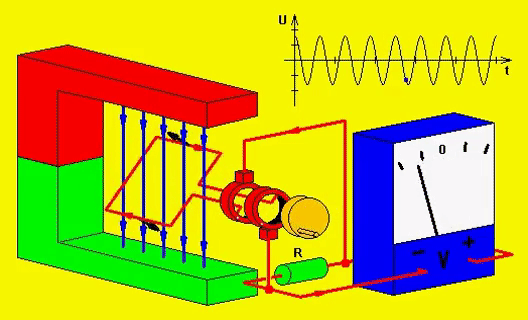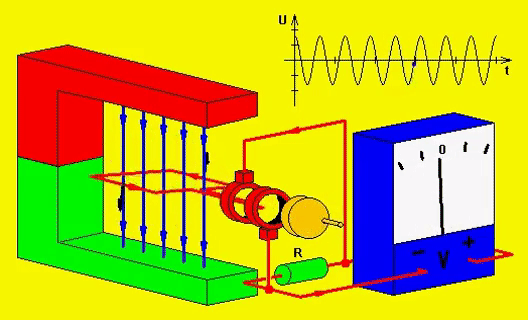

Electricity and magnetism are related to each other. Electricity can be produced in two ways. You can either rotate a copper wire in a magnetic field or you can rotate the magnetic field around the copper wire.
Now how can you produce a magnetic field you might be wondering?
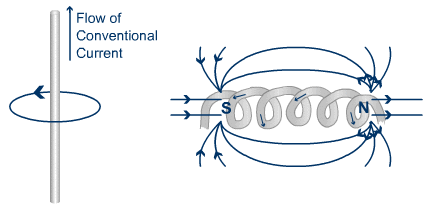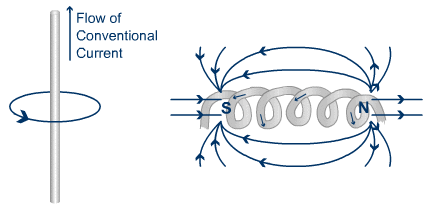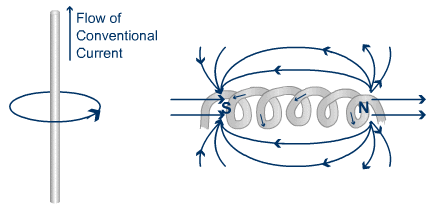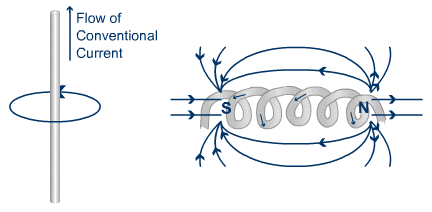

Remember I said earlier that electricity and magnetism are related, here’s how. If electricity or electron passes through any wire, then the magnetic field will form around the wire. And by wounding any wire in a circle, you will get a stronger magnetic field. So this way you can produce a magnetic field.
And the other method of producing a magnetic field is to use permanent magnets which have a natural magnetic field.
In the generator, the stator (stationary part of the machine) has coil windings on it and the DC current (because DC current gives you a strong magnetic field compared to AC current) is passed through those coils and hence the magnetic field is produced around those coils.
The stator here is a shallow drum and the rotor is rotating inside it. The rotor of the generator is inside the stator, and it is rotated using the engine. The rotor also has coil winding on it.
Now the magnetic field is stationary and the coils of the rotating rotor cut the magnetic field; hence, the electricity is induced in the rotor. And if the coils are in a complete circuit (meaning a closed path), then the current will flow in it.
This whole phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction which is developed by faraday.
Countries like the USA and Canada use the 60Hz frequency power, and if this frequency fluctuates even the slightest, then it can permanently damage your appliances.
So in order to produce the 60Hz supply, the engine must rotate the rotor at 3600 RPM speed (which is not the case with the inverter generator). There is a governor in the generator which monitors the speed of the generator and adjusts the speed and this governor is a very important part of the generator.
Working of Generator.
What is ampere, voltage, and watts in the generator?
Many times you have seen that this portable generator is rated for this ampere, volt, and watts. Now, what does that mean?
Voltage, Ampere, and Watts Explained.
Let’s understand this terminology by this example.
Suppose the pump is pushing the water through the hose. Now pump is a generator here that is pumping the electrons out of it. The pump needs some pressure to push the water; this pressure is voltage here. The voltage pushes the electrons to flow through the wire.
In the electrical circuit, these electrons power the appliances. The amount of power consumed by any electrical equipment is measured in watts.
How Electricity Works?
The formula of the watts is Amps x Volts = Watts.
In the USA, voltage is 120 volts so by knowing the current usage of any device you can measure the power consumption of that particular device.
For example, if a device is consuming 10 amps and voltage is 120-volts then the power consumption is 1200 watts.
Read More: Top 10 Best Useful Accessories for Portable Generator
What are starting watts and running watts in a portable generator?
The portable generators are rated by the amount of power they can produce in terms of starting watts and running watts. As the watts of the generator increases, the engine size increases, and hence the weight, noise, fuel tank, and cost also increases.
All the electrical machines with “inductive load” needs additional power at the starting to jump-start the machine, and without this additional power, the machine won’t start. This additional power is known as starting watts, and it is always high than the running watts of the generator.
Example of such machines is refrigerator, oven, air conditioner, television and so on. Resistive loads like light bulb toasters and coffee makers do not require starting watts.
Once the machine has started (be it resistive load or inductive load) it needs some power to run continuously. The running watts is the amount of power your generator can continuously supply.
According to their engine capacity, all the portable generators have different running watts and starting/surge watts. When choosing the generator, you must know how many appliances you want to run using the generator.
That being said, as the generator size increases its noise level also increases. In all of the generators, the inverter generator is one of the quietest generators we have seen so far.




